
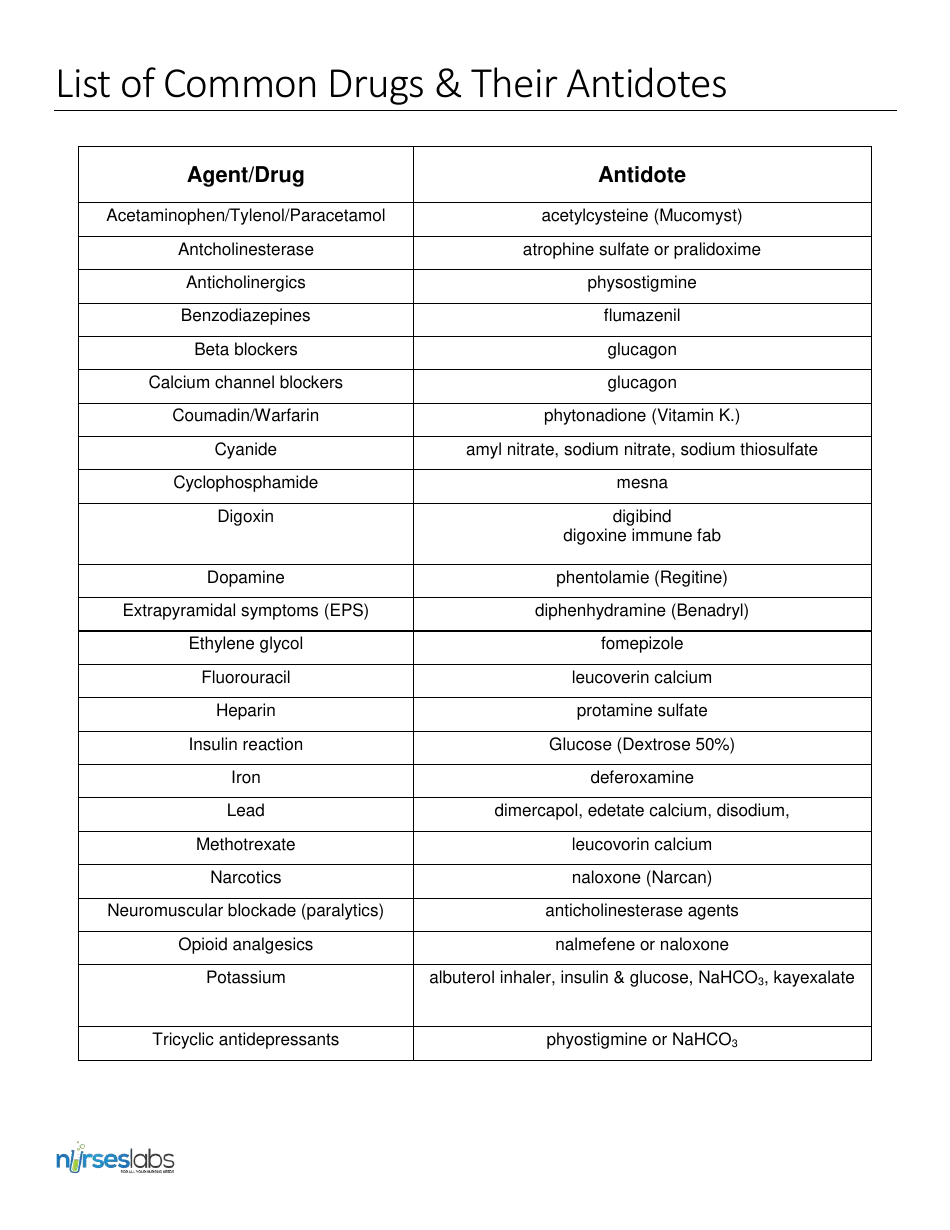

The present data suggest that excess protamine might potentially increase bleeding in the case of severe thrombocytopenia or low factor VIII. Low Molecular Weight Heparin Reversal of Life Threatening Bleeding: Protamine (works just as well with LMWH as heparin) - if with-in 4 hours of dose: 1 mg of protamine for each 1 mg of enoxaparin or 100 units of dalteparin and tinzaparin. Since the administration of protamine is. CONCLUSIONS: We demonstrated that protamine affects the propagation of thrombin generation, which is partially reversed by platelets or increased factor VIII/von Willebrand factor concentrations. But, the determination of protamine in the presence of heparin by optical methods has not been reported so far. In agreement, protamine increased coagulation time evaluated by thromboelastometry significantly more in platelet-poor plasma than in whole blood. A therapeutic concentration of recombinant factor VIIa (60 nM) only affected the lag time of thrombin generation triggered with actin. Low-molecular-weight heparin is commonly used in surgeries to prevent. The addition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor (1.5-3.0 U/mL) to platelet-poor plasma with protamine (24 microg/mL) decreased lag time and increased peak thrombin generation with actin activation. Protamine antidote can be effective in reversing low-molecular-weight heparin. 4 Antidotes and other substances used in. In platelet-rich plasma with platelets at 50 to 200 x 10(3)/microL, protamine (24 microg/mL) prolonged the lag time, but had no effect on peak thrombin generation. Protamine (Sulphate) is used as an antidote of heparin to inhibit the anticoagulant effect of heparin. Protamine also increased lag time and decreased peak of thrombin generation in platelet-poor plasma after tissue factor and actin activation. Curry Living reference work entry Latest version View entry history First Online: 01 January 2016 226 Accesses Abstract Toxicologic events related to therapeutic administration of thrombolytics, heparins, and antiplatelet drugs are far more common than accidental or intentional overdoses. RESULTS: Protamine prolonged prothrombin time and Russell's viper venom time, concentration dependently. In accidental overdoses of heparin, consider t1/2 heparin 60-90 min. Monitor APTT 5-15 min after dose then in 2-8 hr. The reversibility of excess protamine (24 microg/mL) by recombinant factor VIIa or factor VIII/von Willebrand factor concentrate was also tested. 1-1.5 mg per 100 USP units of heparin not to exceed 50 mg. METHODS: We evaluated the effects of increasing protamine concentrations (0 to 24 microg/mL) on prothrombin time and diluted Russell's viper venom time measurements on thrombin generation in platelet-poor and platelet-rich plasma after activation by tissue factor or actin, and on thromboelastometry in platelet-poor plasma and whole blood from 6 healthy volunteers. Protamine sulphate is a basic protein derived from fish sperm that binds to heparin to form a stable salt. BACKGROUND: Protamine sulfate is the antidote for heparin, but in excess it exerts weak anticoagulation. Intravenous protamine sulphate can rapidly reverse the anticoagulant effects of heparin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
